Page 105 - 2022年第53卷第4期
P. 105
0.15 2.5
Pool1 Pool2 Pool3
0.10 Pool4 Pool5 Pool6
2.0
0.05
水位偏差/m 0.00 闸门开度/m 1.5
-0.05
1.0
-0.10 Pool1 Pool2 Pool3
Pool4 Pool5 Pool6
-0.15 0.5
0 8 16 24 32 40 48 0 8 16 24 32 40 48
时间/h 时间/h
(a) 水位偏差 (b) 闸门开度
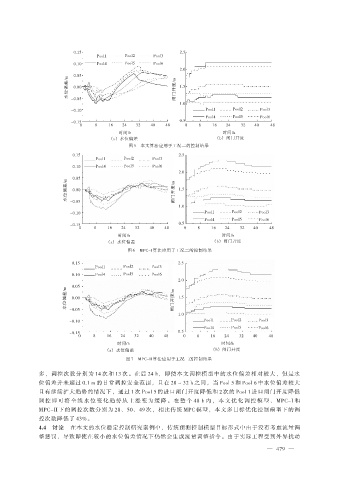
图 5 本文算法应用于工况二的控制结果
0.15 2.5
Pool1 Pool2 Pool3
0.10 Pool4 Pool5 Pool6
2.0
0.05
水位偏差/m 0.00 闸门开度/m 1.5
-0.05
1.0
-0.10 Pool1 Pool2 Pool3
Pool4 Pool5 Pool6
-0.15 0.5
0 8 16 24 32 40 48 0 8 16 24 32 40 48
时间/h 时间/h
(a) 水位偏差 (b) 闸门开度
图 6 MPC-I 算法应用于工况二的控制结果
0.15 2.5
Pool1 Pool2 Pool3
0.10 Pool4 Pool5 Pool6
2.0
0.05
水位偏差/m 0.00 闸门开度/m 1.5
-0.05
1.0
-0.10 Pool1 Pool2 Pool3
Pool4 Pool5 Pool6
0.5
-0.15
0 8 16 24 32 40 48 0 8 16 24 32 40 48
时间/h 时间/h
(a) 水位偏差 (b) 闸门开度
图 7 MPC-II 算法应用于工况二的控制结果
多,调控次数分别为 14 次和 13 次。在后 24 h,即使本文调控模型中的水位偏差相对较大,但是水
位偏差并未超过 0.1 m 的日常调控安全范围,且在 28 ~ 32 h 之间,当 Pool 5 和 Pool 6 中水位偏差较大
且有继续扩大趋势的情况下,通过 1 次 Pool 5 的进口闸门开度降低和 2 次的 Pool 1 进口闸门开度降低
调 控 即 可 将 全 线 水 位 变 化 趋 势 从 上 涨 变 为 缓 降 。 在 整 个 48 h 内 , 本 文 优 化 调 控 模 型 、 MPC-I 和
MPC-II 下的调控次数分别为 28、50、49 次,相比传统 MPC 模型,本文多目标优化控制模型下的调
控次数降低了 43%。
4.4 讨论 在本文的水位稳定控制研究案例中,传统预测控制模型目标形式中由于没有考虑流量调
整惩罚,导致即使在较小的水位偏差情况下仍然会生成流量调整指令。由于实际工程受到外界扰动
— 479 —